By Apollo Seiko
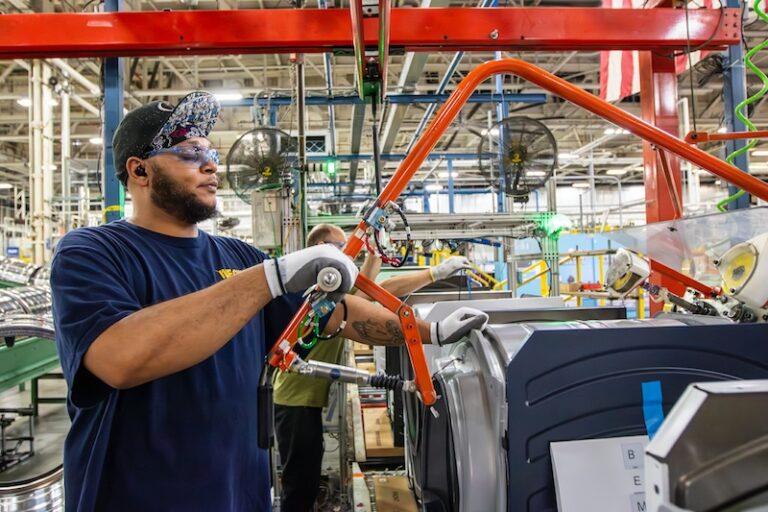
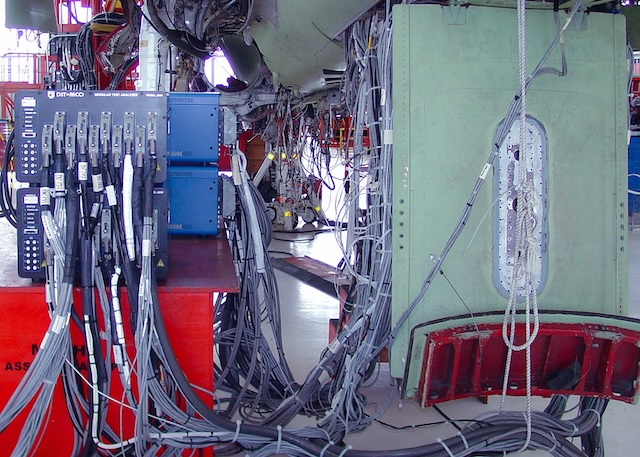
Soldering has long been considered a method of choice in the joining of electronic components to wire leads. When properly executed it produces a dependable connection that is vibration resistant and able to survive corrosive environments. Automation has advanced this process even further by eliminating the inconsistencies of hand-assembly. A soldering robot will unfailingly apply the same amount of solder, the correct amount of heat and produce an extremely precise solder joint. Furthermore, hand soldering has a reputation for being more costly than other forms of wire connecting while automating this process has proven to greatly reduce costs and material waste. Also, in the past 3-5 years hiring skilled hand solder operators has become exceedingly difficult.
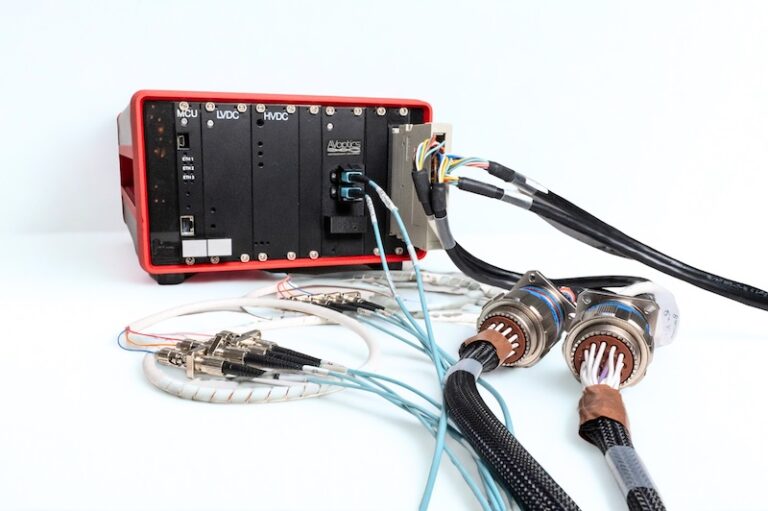
Robotic soldering also resolves issues with high conductor counts and unique solder alloys.
Automated soldering solutions provider Apollo Seiko Ltd., in Bridgman, MI has experienced great success soldering notoriously problematic Nitinol alloy wires. Nitinol is favorably used in the manufacturing of stents, catheters, and heart valve replacements as well as other endoscopic instruments. It is revered for its shape memory and super elastic characteristics. This remarkable material is also able to change shape and length as a response to temperature changes or at the introduction of an electrical current. Due to the nature of Nitinol there are some additional engineering challenges to overcome. One of the biggest obstacles is the intrinsic titanium-oxide-rich exterior layer of the alloy that hinders access and bonding ability for the molten solder. Fortunately, advances in flux formulas have yielded both flux, solder wire and solder paste products that are able to remove the surface oxides and wet the solder to the surface. Apollo Seiko has had great success using these special flux products to attach Nitinol catheter wires to stainless steel components.
In addition to advanced alloys, electronics manufacturing is seeing a shift toward miniaturized wires and components. Apollo Seiko is providing laser soldering solutions to meet the technical challenges of nanosized component assembly. These laser soldering robots are capable of producing micro-sized laser beams for applications deemed otherwise too small for traditional soldering and assembly methods. Advanced optical technology provides a reliable solution for micro and narrow pitched parts frequently used in high-density electronic equipment. This method is also good for soldering circuit boards that must withstand harsh environments. Because the energy intensity of the laser can be precisely adjusted, the risk of damage to peripheral components is minimized.
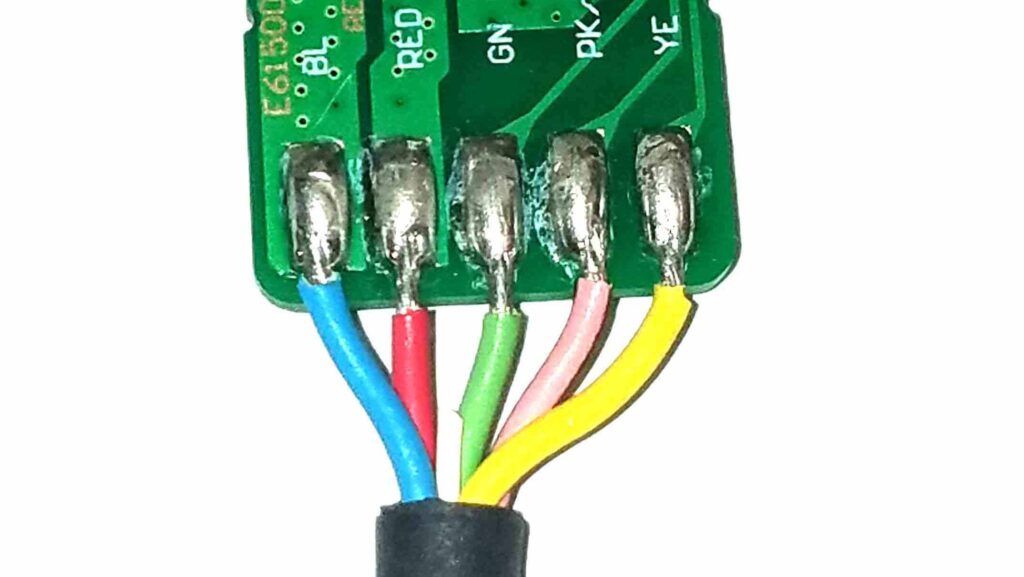
Applications featuring unique alloys and unusually small components are not the only projects that benefit from automated soldering. Apollo Seiko has been able to provide the optimum solution for traditional wire lead assemblies such as filling solder cups on connectors, soldering thru-hole and SMT style wire leads to PCB’s, and soldering wire leads to USB connections.



These more traditional applications are typically accomplished with the use of iron tip soldering systems. These robots feature advanced accessory items such as temperature control units, position calibration units and highly engineered wire feeders. Apollo Seiko wire feeders have built- in roulette cutting blades. These blades perforate the soldered wire to expose the flux core. This prevents solder balls, which are formed when molten flux bursts free of the solder wire as it touches the hot iron tip. If the wire is pierced prior to reaching the tip, the flux can outgas from the wire before the solder melts, preventing solder splatter which can be dangerous to the integrity of electrical components. It also provides consistent flux coverage allowing the solder to melt on a clean, active surface.

Automated soldering technology continues to advance well beyond wire feeding innovation. Apollo Seiko recently introduced their new ARC 5000 option. The ARC 5000 provides the ability to adjust the angle of the iron soldering unit using an auxiliary access function. This allows for the iron unit to tilt and position itself on a 5th axis beyond the standard range of movement. For more information about this new technology or to find out more about how automated soldering may benefit your assembly process please visit www.roboticsoldering.com.
Last year, 2019, marked 50 years of soldering excellence for Apollo Seiko. They are a global company with locations in 10 different countries. In addition to traditional soldering methods, they feature a specialized laser soldering system, sleeve soldering for desktop or inline as well as a new AF Series for in-line or off-line selective flow. From automotive to biotechnology, Apollo Seiko believes all electronics industries can benefit from automated soldering. Meet us in person at the IPC APEX EXPO in Booth #2051.