By Rob Iversrud, Product and Category Manager, Waytek
When installing or maintaining electrical wiring on boats, it is important to follow guidelines specific to marine vessels, which are stringent due to harsh operating environments. Here are some key regulations and guidelines that govern marine electrical wiring.
Legal Regulations
The ABYC (American Boat and Yacht Council) develops standards for marine vessels, including electrical systems. It’s widely accepted in the United States for both consumer and commercial vessels. The standard “ABYC E-11: AC & DC Electrical Systems on Boats” provides guidelines covering proper wire sizing, grounding, protection against short circuits, and more.
U.S. Coast Guard (USCG) standards also apply, particularly for commercial vessels. The USCG enforces specific rules for electrical systems on boats, which align closely with the ABYC standards.
Title 46 of The Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) governs maritime operations in the U.S. This includes electrical installations for commercial vessels, with specific requirements based on vessel size and application.
- 46 CFR Subchapter T includes electrical guidelines for small passenger vessels (less than 100 gross tons).
- 46 CFR Subchapter H covers large passenger vessels over 100 tons.
- 33 CFR Part 183 covers safety standards for electrical systems in recreational boats.
Larger commercial vessels, especially those used internationally, need to comply with SOLAS (Safety of Life at Sea) regulations and International Maritime Organization (IMO) guidelines.
Industry Guidelines and Best Practices
- Wire Type and Insulation: Use marine-grade tinned copper wire with appropriate insulation for resistance to moisture, salt, oil, and chemicals. Avoid household wiring on your boat. For more information, see the section below on UL 1426 certifed wire.
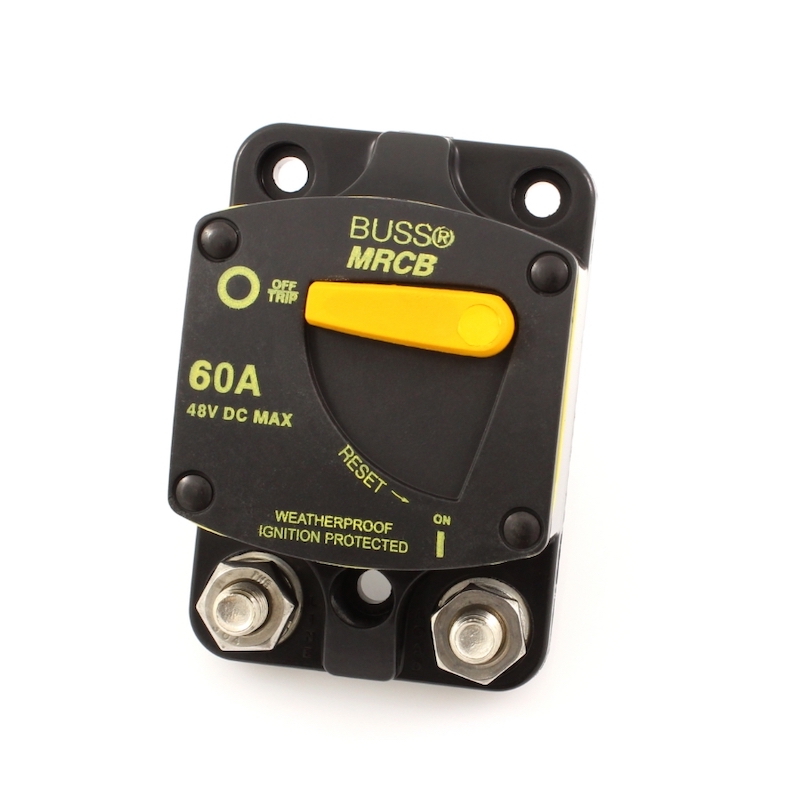
- Circuit Protection: All circuits must be protected by fuses or circuit breakers. Use marine-rated equipment that can handle vibration and corrosion. Right: Marine-rated battery fuses and circuit breakers from Eaton.
- Grounding and Bonding: Proper grounding is critical to prevent electrical shocks, fires, and hazards such as electrostatic discharge. ABYC standards provide specific grounding requirements for both AC and DC systems.
- Marine Battery Installations: Batteries should be installed in ventilated areas (because they generate hydrogen gas when recharging) with secure mounting and proper isolation switches.
- Color Coding and Labeling: ABYC standards provide color codes for wiring to make it easier to identify and troubleshoot electrical systems. For example, yellow for DC ground, red for DC positive, and black for AC neutral.
- Voltage Drop: ABYC recommends limiting voltage drop to 3% for critical circuits (e.g., navigation lights, bilge pumps) and 10% for non-critical circuits.
- Equipment Certification: Ensure that all electrical equipment and components meet UL Marine Standards (Underwriters Laboratories), which will ensure safety and performance for the marine environment.
- Waterproofing and Sealing: All electrical connections should be sealed with heat-shrink tubing or waterproof connectors to prevent corrosion and water intrusion.
Use of UL 1426 Certified Wire & Cable
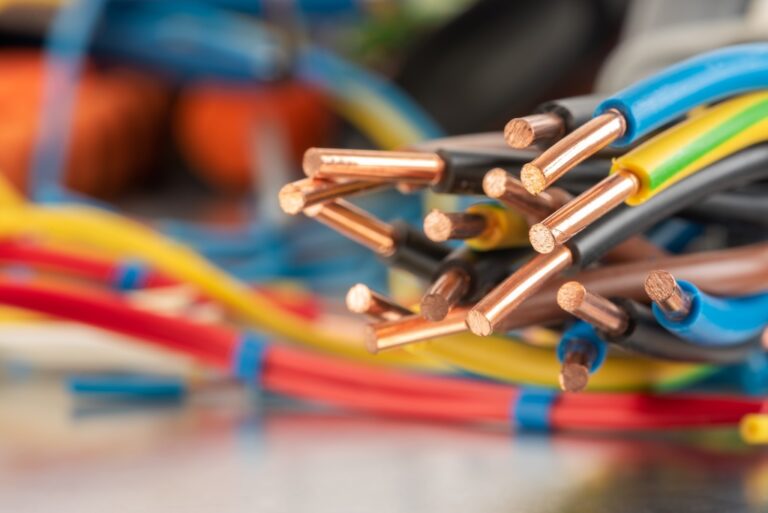
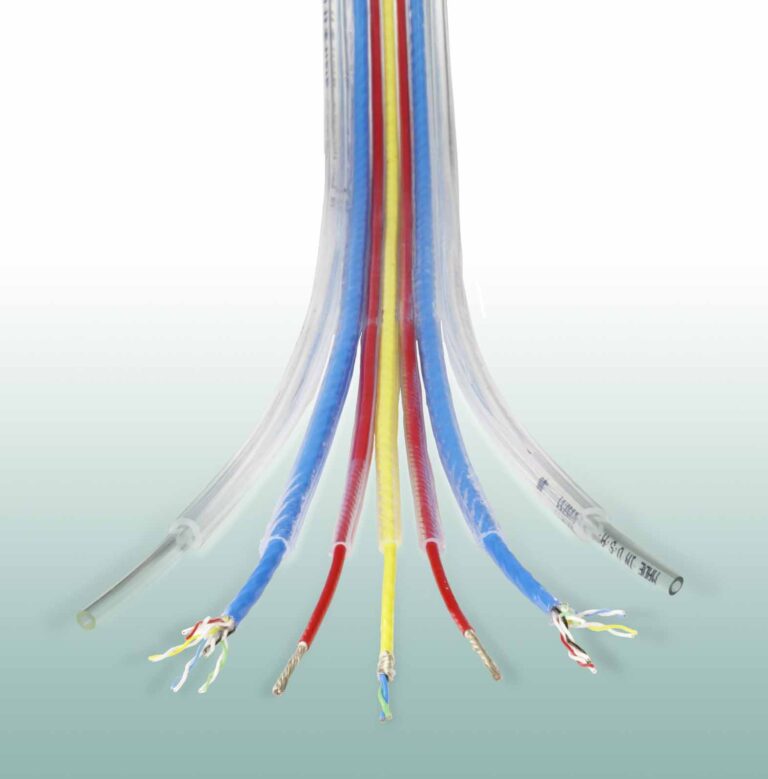
UL 1426 is a critical standard for electrical wiring in boats. It covers cables for boats and ensures that the wiring used in marine environments meets strict safety, performance, and durability requirements. The standard applies to insulated boat cables, which are essential in marine electrical systems (Figure 1).
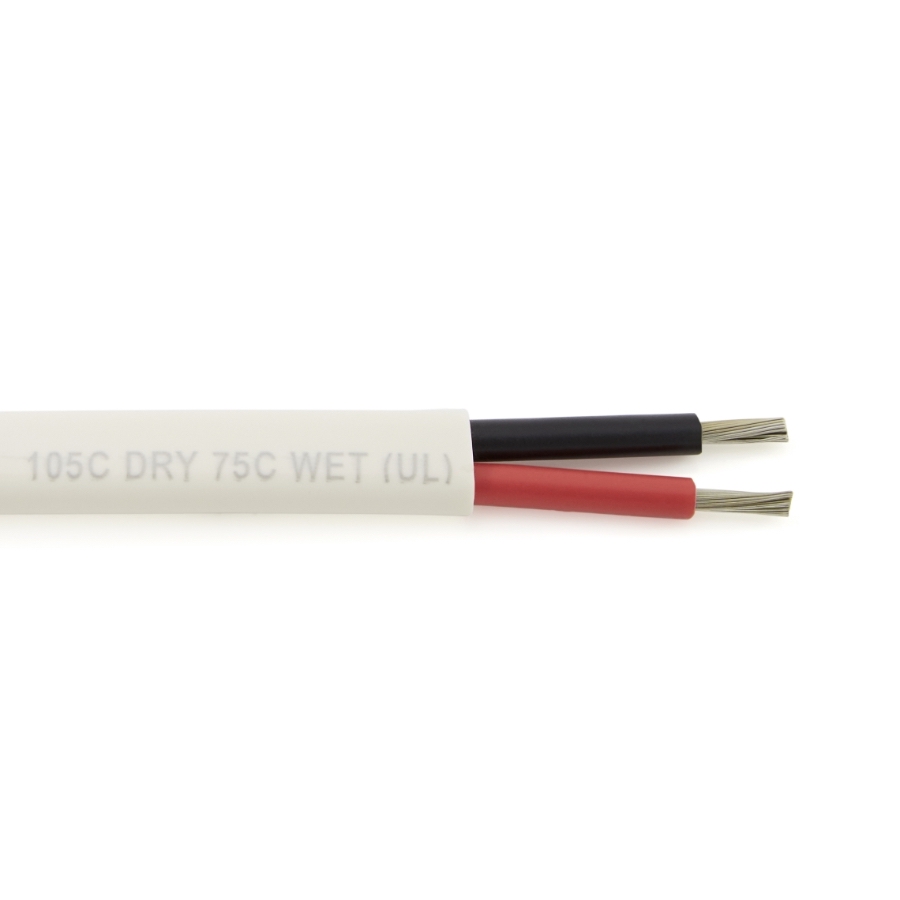
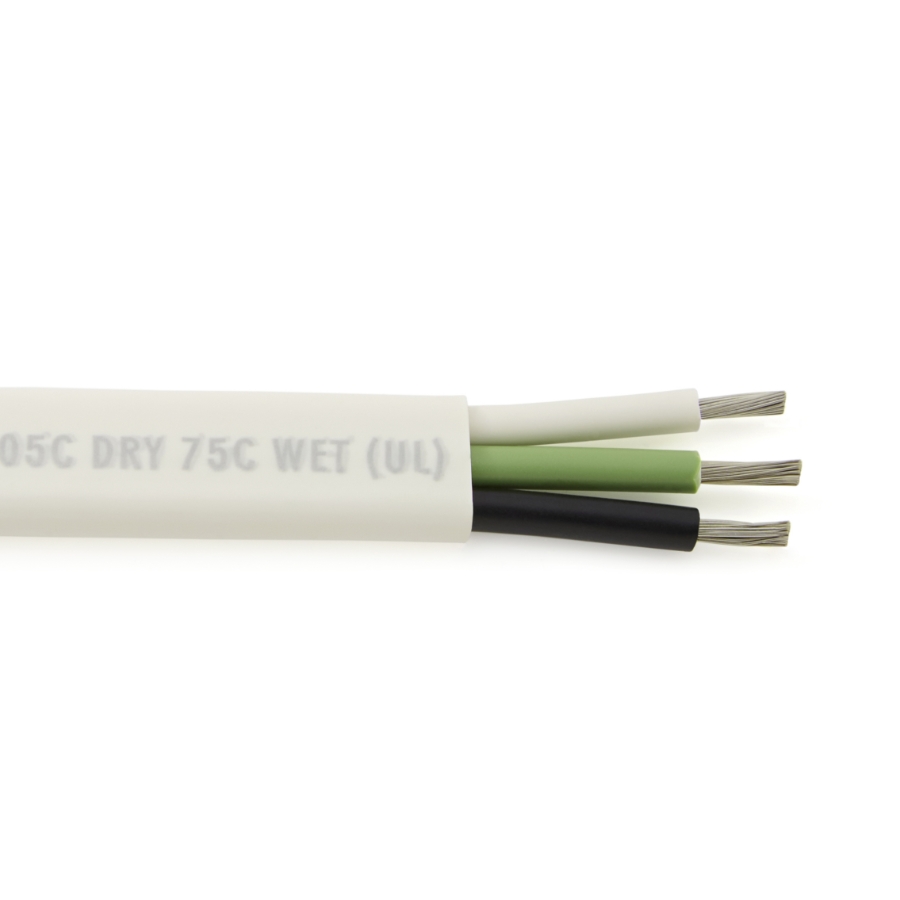


UL 1426 ensures that the wire used in boats is marine grade, meaning it is designed to withstand the unique challenges of the marine environment including corrosion from salt water, excessive motion and vibration, and exposure to heat and flame.
Key features of UL 1426 wiring include use of tinned copper conductors for corrosion resistance, high temperature ratings (typically up to 105°C), flexible insulation that is resistant to oil, fuel, water, and chemicals, and industry-standard color coding for marine wiring (e.g., red for positive, black for negative in DC systems).
Cables that meet UL 1426 standards provide reliable electrical performance while minimizing voltage drop over longer distances. This is essential for ensuring proper operation of critical onboard systems like navigation lights, pumps, and communication equipment. Using UL 1426-certified wiring reduces the risk of electrical shorts, fires, or failures, especially in wet or submerged conditions.
SAE J1171: The Importance of Ignition Protection
SAE J1171 is a standard established by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) that specifies the requirements for ignition protection of electrical components in marine environments. It applies to devices that are installed in areas where explosive or flammable gases (like fuel vapors) may be present, such as in engine rooms or bilge spaces on boats.
Electrical devices must be certified as “ignition-protected” to ensure they will not produce sparks or heat that could ignite fuel vapors. Compliance with SAE J1171 ensures that equipment is safe for use in such hazardous areas.
SAE J1171 applies to many electrical components, especially those close to fuel tanks or engines. Some common examples include:
- Bilge pumps and blowers.
- Alternators and starters for marine engines.
- Electric motors used in various onboard systems.
- Battery isolators and switches near gasoline engines.
In many cases, SAE J1171 certification is not just a best practice but a legal requirement. The U.S. Coast Guard mandates that all electrical components used in potential gasoline vapor environments must comply with SAE J1171. The ABYC also mandates that such components must be ignition-protected as defined by SAE J1171 or equivalent standards. (Learn more about Ignition Protection for electrical components in the article Ignition Protection: Why It Matters on the Waytek website.)


Other International Standards
Other standards such as IEC 60092: International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards for electrical installations on ships, may be required for larger vessels, especially those operating internationally.
International standards for small craft electrical systems, governing DC installations on recreational boats under the ISO system, are provided in ISO 13297.
Conclusion
By following these guidelines and ensuring compliance with national and international regulations, you can install and maintain electrical systems in boats that meet safety and performance expectations. Regular inspections and adherence to updates in standards will also help maintain compliance.
Investing in compliant, high-quality marine components like UL 1426-certified wiring and SAE J1171-certified ignition-protected equipment can yield significant long-term savings. Certified materials may carry a higher initial cost, but they reduce the likelihood of costly failures, maintenance needs, and safety issues. Products like marine-rated battery isolators or fuses—essential for ABYC and USCG compliance—contribute to system reliability and can offset costs over time through reduced downtimes and repairs.
About Waytek
Waytek, Inc. is a customer-driven distributor of automotive wire and DC electrical components serving OEMs (original equipment manufacturers), wire harness manufacturers, and upfitters across North America. A family-owned business founded in 1970, Waytek commits to providing exceptional service to our customers, shipping more than 99.5 percent of in-stock orders the same day.