Diesel Locomotive Cable (DLO)
What Is Diesel Locomotive Cable?
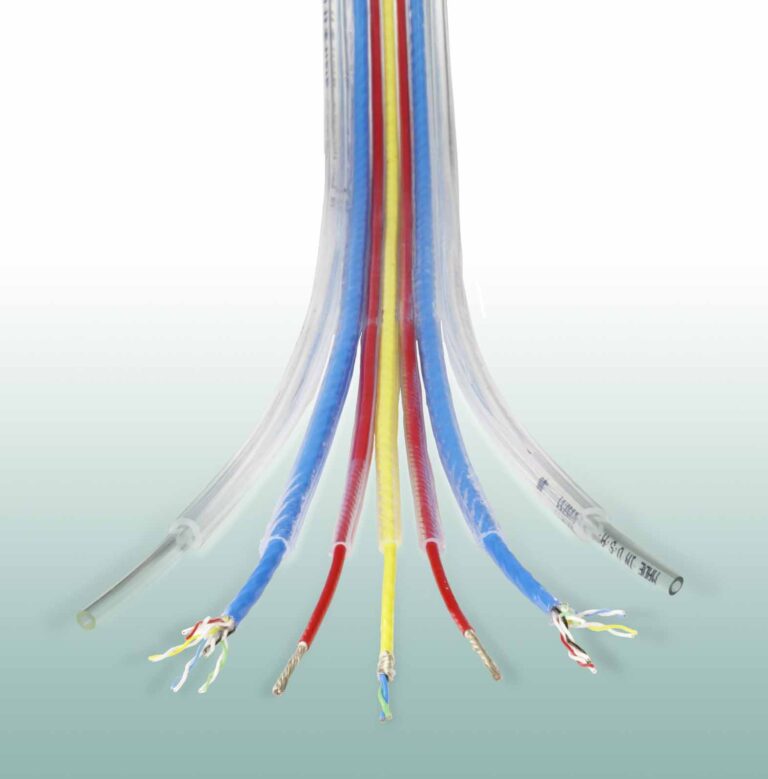
Diesel locomotive cable (DLO) is a flexible cable with a dual-extruded product consisting of ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) insulation and a thermoset chlorinated polyethylene rubber (TS-CPE) jacket. DLO comes with tinned copper Class I stranded conductors. The voltage rating for DLO cable is 2000 volts. DLO cable is suitable for use in conduit, ducts, troughs and electrical tray. It can be used in wet or dry areas. The maximum continuous conductor temperature for normal operations is 90°C in dry locations and 75°C for wet locations. Today, there are several manufacturers that are making DLO cable with a UL RHW-2 rating, which gives the cable a 90°C wet or dry rating. DLO has excellent resistance to oils, acids, alkalis, heat, flame and has outstanding abrasion resistance.
Diesel Locomotive Cable Applications
DLO today is a UL-listed cable originally developed to supply power to traction motors of the diesel-electric locomotives. Despite having the word diesel in the name, diesel locomotives use electricity to drive the forward motion. A large diesel engine turns a shaft that drives a generator, which makes electricity. This electrical energy powers large electric motors at the wheels, called traction motors.
Some locomotives use DC generators and others use AC. Modern alternating-current locomotives have better traction and adhesion and are used on trains that carry heavier loads. DC is still sometimes used because it is less expensive to manufacture. DLO cable is used to transmit the power from the generator to the electric-drive motor. It is available in conductor sizes ranging from 14 AWG to 1111 kcmil. It is also used in many other applications where a flexible, tough cable is needed due to tight bending radii.
DLO cable is recommended as a portable cable for drilling rigs, on-shore and off- shore applications, railroad and transit car wiring, and electric earth-moving equipment. It also extremely well-suited for other applications like shipyards, power and control jumper cables, motor leads, and sometimes as a telecom power supply.
Due to DLO cable carrying a UL RHH/RHW-2 or CSA RW90 rating, the AHJ (authority having jurisdiction) will allow its use in many other applications. These may include other electrically driven moving equipment, motor or power leads, UPS backup systems, fuel cell systems, battery banks and backup generators. DLO cable in sizes 1/0 AWG and larger is generally cable tray rated, allowing for use in industrial facilities. DLO cable may be an allowable substitute for welding cable. DLO can be thought of as a very heavy-duty welding cable due to the dual construction (insulation and jacket) and will at times be used as welding cable, especially for high-current applications. Welding cable is not to be used a substitute for DLO; it is generally only allowed on the secondary circuits of an electric welder as part of welding leads.
How to Terminate Diesel Locomotive Cable
The major lug manufacturers offer special lugs for finely stranded cable, called flex lugs. These lugs are required for DLO cable, welding cable, Type W, G, G-GC and SHD-GC cable. Section 110.14 of the 2017 NEC requires that conductors more finely stranded than ASTM Class C be terminated in specially identified connectors. Care should be taken by users when stripping the cable in preparation for termination to not allow the fine stranding to become frayed. Most barrel-compression lugs sized for DLO cable have a chamfered barrel to help guide the conductor into the barrel. Be careful to not break off any of the strands when stripping the insulation and jacket or allow any of the strands to bend back on themselves.
DLO cable is heavy and expensive compared to more common copper power cable, such as THHN or XHHW, due to the labor that goes into producing the fine stranding and the more expensive insulation compounds and curing methods. DLO is a premium product that provides many benefits in the appropriate use case.
| Gauge Size (AWG/kcmil) | Welding Cable (600 V) | UL Style 1283 (8–2 AWG)5 UL Style 1284 (1 AWG–500 kcmil)6 | DLO (2,000 V) | Type W (2,000 V) | ||||
| Insulation Thickness (in.)* |
Strand Count* |
Insulation Thickness (in.) |
Strand Count* (multiple options) |
Insulation Thickness (in.)7 |
Strand Count* | Insulation Thickness (in.)8 |
Strand Count* |
|
| 8 | — | — | 0.060 | — | 0.055 (0.085 w/jacket) |
37 | 0.060 | 133 |
| 6 | 0.070 | 259 | 0.060 | 19/133/266 | 0.055 (0.085 w/jacket) |
61 | 0.060 | 133 |
| 4 | 0.070 | 413 | 0.060 | 19/133/420 | 0.055 (0.085 w/jacket) |
105 | 0.060 | 259 |
| 2 | 0.070 | 651 | 0.060 | 19/133/665 | 0.055 (0.100 w/jacket) |
147 | 0.060 | 259 |
| 1 | 0.070 | 840 | 0.080 | 133/259/833 | 0.065 (0.110 w/jacket) |
224 | 0.080 | 259 |
| 1/0 | 0.090 | 1050 | 0.080 | 259/1064 | 0.065 (0.110 w/jacket) |
266 | 0.080 | 259 |
| 2/0 | 0.090 | 1323 | 0.080 | 259/1330 | 0.065 (0.110 w/jacket) |
323 | 0.080 | 259 |
| 3/0 | 0.011 | 1666 | 0.080 | 259/1330/1672 | 0.065 (0.110 w/jacket) |
418 | 0.080 | 259 |
| 4/0 | 0.011 | 2107 | 0.080 | 259/551/2109 | 0.065 (0.130 w/jacket) |
532 | 0.080 | 259 |
| 250 (DLO:262.6) | 0.125 | 2450 | 0.095 | 2451 | 0.075 (0.140 w/jacket) |
646 | 0.095 | 427 |
| 300 (DLO:313.3) | 0.125 | — | 0.095 | 3458 | 0.075 (0.140 w/jacket) |
777 | 0.095 | 427 |
| 350 (DLO:373.3) | 0.125 | 2350 | 0.095 | — | 0.075 (0.140 w/jacket) |
925 | 0.095 | 427 |
| 400 | 0.125 | — | 0.095 | — | — | — | 0.095 | 427 |
| 450 (DLO:444.4) | 0.125 | — | 0.095 | — | 0.075 (0.140 w/jacket) |
1110 | 0.095 | 427 |
| 500 (DLO:535.2) | 0.125 | 5054 | >0.095 | — | 0.075 (0.140 w/jacket) |
1332 | 0.095 | 427 |
| *Common construction, subject to change per manufacturer | ||||||||
Table 1: Insulation Thickness and Strand Count of Common Flexible Cable