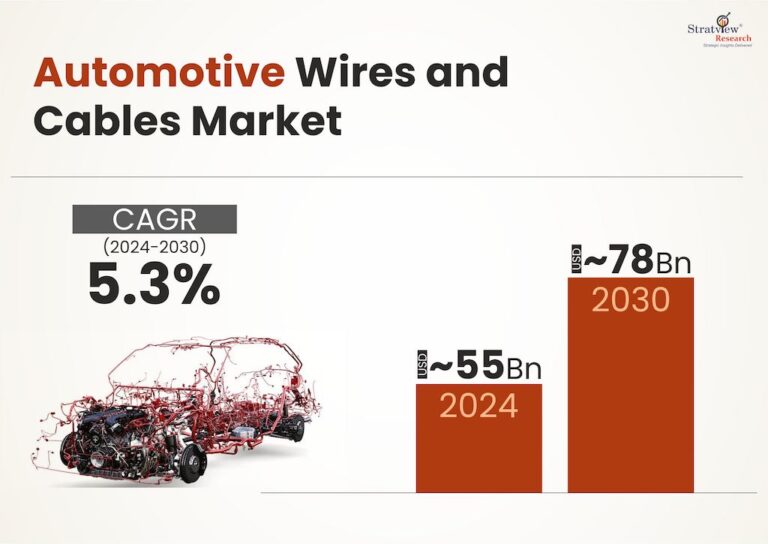
How To Select a Polymer for High Temperature Wire and Cable
High temperature wire and cable applications are getting more and more prominent. Its use and popularity have followed the trajectory of technology refinement over the past 100 years.
Advancements in technologies like robotics, AI and 5G favor the use of high temperature wire and cable because of its smaller size, long length availability*, along with excellent chemical, mechanical and electrical properties.
The original high-temperature wire insulation was PTFE. It was discovered by a DuPont scientist back in the 1930s. Through the years, it became the de facto solution for high-temperature environments and its popularity grew with military and aerospace applications. It is still popular today due to its special properties and the fact that it enjoys some long-standing military approvals and drawing inclusions.
When placing an order for wire and cable, most harness manufacturers wish to order the longest length they can buy. The longer lengths will save them a lot of scrap and cost in manufacturing. A big problem with PTFE is that it is difficult to get in relatively long lengths due to manufacturing challenges. Therefore, Dupont invented the PFA, FEP, ETFE copolymers of PTFE which can be produced in longer lengths to replace some of the high temperature applications
Another problem with PTFE is that it is not melt-processable. It requires special mixing with a lubricant to create a paste extrusion without melting. It is then sintered at a high temperature to get rid of lubricant. By contrast, all PFA, FEP, ETFE and ECTFE materials are melt-processable; meaning you can use a conventional melt extruder. There are fewer steps as the material is simply melted, and the polymer is coated over the copper wire, thus reducing cost.
Engineers need to be aware of the different characteristics, properties, cost etc. of these high temperature polymers in order to design a wire or cable which is suitable for their products in the modern world.
Here are some lists of high temperature fluoropolymers:
- PFA (perfluoroalkyl) is a fluoropolymer which has very similar properties to PTFE. It is melt-processable for low cost, is available in long lengths, and has a three times higher dielectric strength over PTFE. PFA has excellent electrical, chemical and mechanical properties. The biggest advantage of PFA is its high temperature rating at 250°C (per UL)
- FEP (Fluorinated ethylene propylene) is copolymer of hexafluoropropylene and TFE. It is melt-processable at an even lower cost than PFA. It has similar electrical, chemical and mechanical properties and is available in the longer lengths. The temperature rating is 200° C (per UL). The main advantage of FEP is its low cost compared to PFA.
- ETFE (ethylene tetrafluoroethylene) a fluoropolymer with similar properties as PTFE but is melt-processable with excellent mechanical, radiation resistance, light weight and is available in long lengths. The dielectric constant is 2.6 which is not as good as PTFE, PFA or FEP at 2.0. Flexibility is poorer than PFA and FEP, but it has better abrasion and better cut-through resistance. The temperature rating is 150° C (per UL). The advantage of ETFE is its radiation resistance, toughness and light weight.
- ECTFE (ethylene chlorotrifluoroethylene) is a fluoropolymer with similar properties as PTFE but is more melt processable with lowest cost. It has great mechanical properties, is light weight, and is available in the longest length of these four materials. The dielectric constant is 2.6 which is not as good as PTFE, PFA, FEP at 2.0. Flexibility is poorer than PFA and FEP, but it has better abrasion and cut-through resistance properties. The temperature is 150° C (per UL). The advantage of ECTFE is its similar to ETFE but at a lower cost.
Conclusion: The above fluoropolymers are all excellent materials for today’s high-temperature wire and cable applications. They share excellent chemical, mechanical, electrical properties, long length availability, are small size and available at a relatively low cost. They match perfectly for today’s technology demands and they are all UL approved.