A Welding Machine For All Terminals
by Saeed Mogadam – Telsonic
Utilization of ultrasonic metal welding, especially for wire/cable terminations has become increasingly popular and accepted by the automotive industry. Both wire harness manufacturers and OEMs have gained more knowledge on the technology and, as a result, have made substantial progress in product development of connectors. The suppliers of welding equipment, in the meantime, have made significant contributions to this growth by making continuous advancements in the technology. The introduction of a new connector for any automotive application starts with the product designer and ends with the best solutions from the equipment supplier. Factors influencing the welding feasibility and its quality are illustrated in figure 1. The process of design and material selection, along with the plating conditions, is the responsibility of the connector manufacturers. However, the equipment supplier must make sure that the welding process, equipment, and the human interface, is made simple, yet consistent and easy to maintain. This process of close collaboration between the connector manufacturer and the welding machine supplier is an established process. Thus, the Ultrasonic metal welding process for wire harnesses and cable terminations/assemblies is more acceptable than ever.
Factors influencing the weld quality
Figure 1: Factors influencing the weld quality
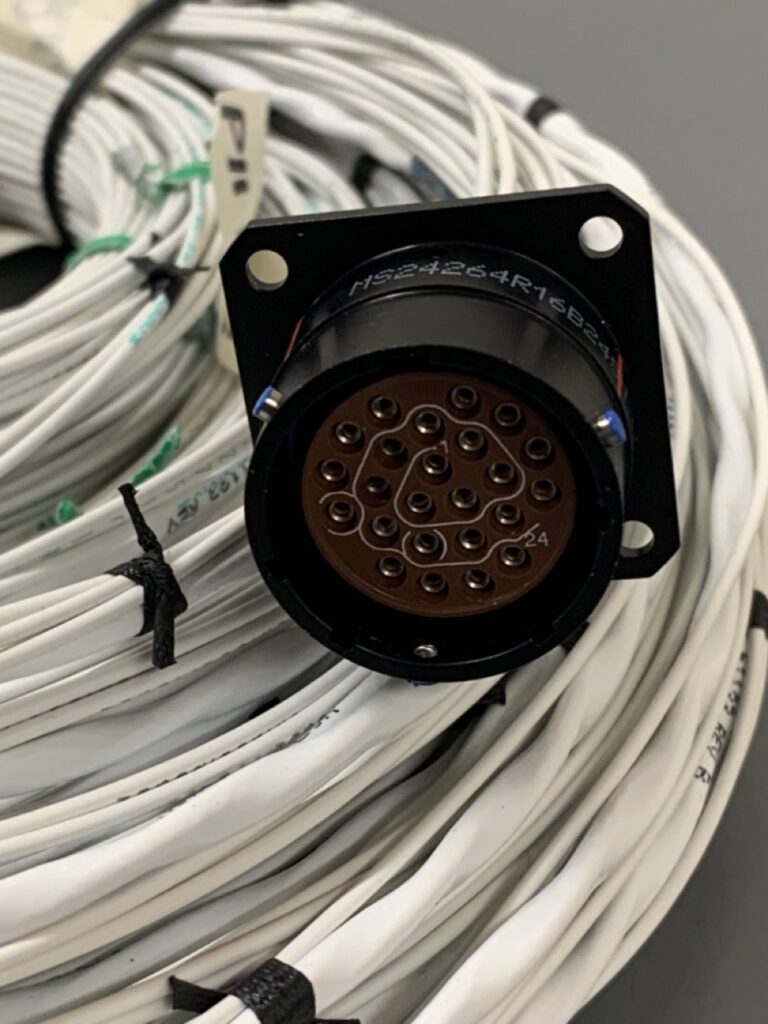
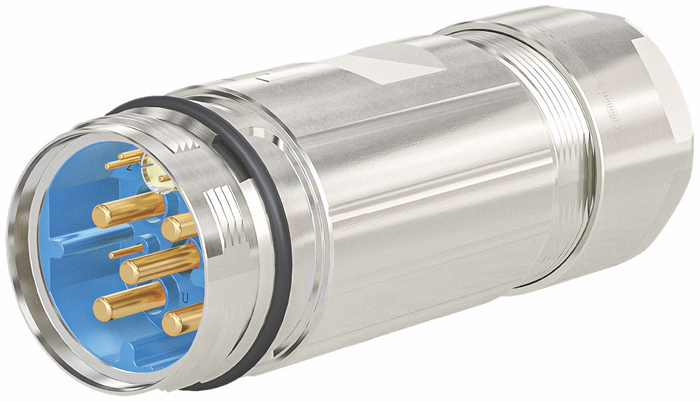
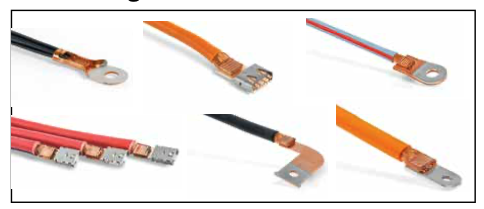
Today, new terminals in all different shapes and forms are being designed and utilized for automotive applications. The latest and most common applications are for high voltage cable terminations and battery cable assemblies. Such a variety in the automotive terminal designs has heightened the demand for universal welders. A universal welding machine must be simply adaptable to most terminals, if not all. Such welding equipment allows manufacturers to utilize the same machine for a wide spectrum of designs and manufacturing process requirements. And yet, the universal welder must be able to do a variety of terminations with minimal change-over, tooling replacement and stringent quality control.
To address these developing requirements, the universal welder must be designed with standardized flexible modules to make the adaption to every termination very simple on the same machine. All modules must be capable of controlling the process with quality standards such as USCAR38 and with minimal change-over or replacement.
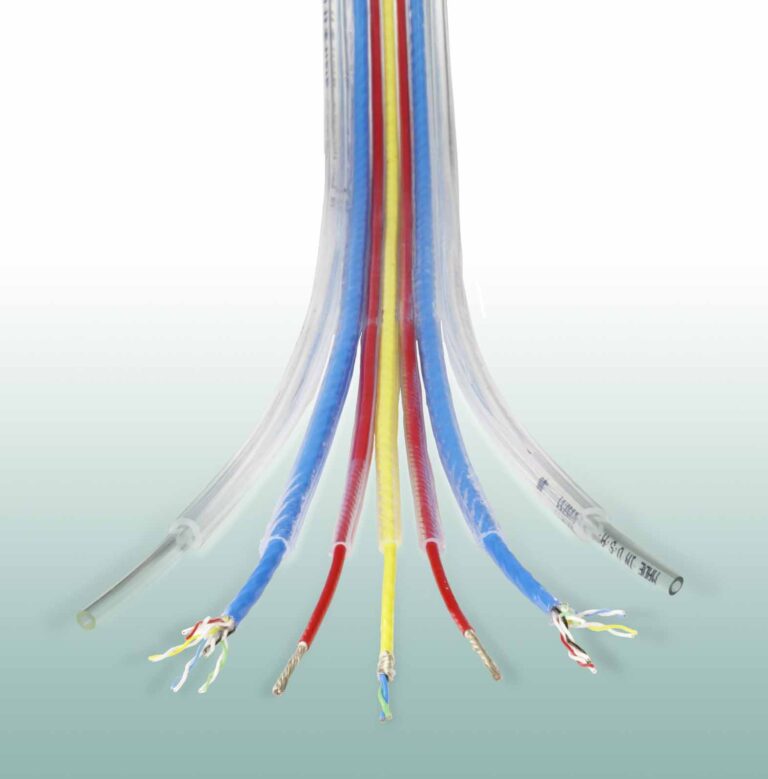
The MPX-TC universal welder was developed by Telsonic to meet the industry demands for simplicity and consistent quality. The machine works on the principles of longitudinal vibrations which is most common in the industry. The machine is available with a wide range of power offerings from 2.4 KW to 7.2 KW for copper cables up to 50 mm². The images below illustrate the variety of terminals commonly used in the industry today.
In its simplest form, a universal system can be a benchtop welding machine for battery applications or any spot welding. At the same time by adding standardized modules, the MPX can perform manual operations for terminations as well as complex tasks such as semi-automatic terminations and more. These modules are designed to be robust and allow for 24/7 operations. Once the terminal design is defined and accepted to be feasible, the MPX can simply be configured by adding standard and/or optional modules (possibly just two components) to complete a fully functional machine.
The MPX universal welding machine advantages are:
- Minimal changeover for similar terminals or perhaps different size cables with the same terminal.
- Easy integration of modular subassemblies when terminals require additional steps such as insulation crimping or automatic feeding.
The flexibility of the MPX allows the manufacturer to utilize the same machine for many different terminals. For high volume production, the machine is common to all applications and allows the plant staff to be easily trained on the operation, and quality control, while using fewer parts. The maintenance of the equipment on the manufacturing floor is thereby reduced and simplified. All welding and quality control parameters can be transferred among machines. The standardization of the machines offers better quality, interchangeability, higher production rate, lower maintenance, and overall effective manufacturing costs. This machine is also ideal for application development and feasibility at customers’ sites or at Telsonic application laboratory. Furthermore, customers will have the advantage of shorter manufacturing and delivery time.
Specific configurations of the machine are defined by the terminal design (Flat, 3D, with side walls) and process requirements. Here is the view of the MPX-TC with all standardized module and options for different terminals and requirements.

– Basic Machine for Flat terminals with or without walls – Terminal Feeding Module
– Crimper Module
Standard modules in MPX-TC consists of:
- The MPX actuator: the welding system
- The gather mechanism, also known as downholder: this is to control the width of the weld nugget according to the USCAR 38 requirements
- Anvil fixture: acoustically designed to be universal and have minimum deflection during welding
- Cable stop to control the weld position: two vertical and horizontal motions for all terminals
- Bad weld cutter (optional): this is a requirement by some standards, where the bad weld needs to be cut automatically
- Cable clamp: to hold and position the single or bundle of wires during welding
- Gather inserts with single vertical motion are universal for all flat terminals. For the terminals with walls, the gather inserts are slightly different. The single vertical motion is for faster cycle time and less adjustment.
Custom tools and optional modules are fewer, compared to any other welding equipment
Different cable sizes might require a different size sonotrode (horn). Also, when terminals are geometrically different, then one should design the nest to position/load the terminal correctly each time. Therefore, the only custom tools that one needs for different situation are mostly the sonotrode and nest.
Common applications used by industry
In cases of flat terminals with different cable sizes, the machine requires just the nest and sonotrode for change-over.

3D flat terminal with 35 mm² cable
Terminals with walls require gather inserts with recess in addition to the sonotrode and nest.
Royal Power Solutions terminal with wall and 16 mm² copper cable. High power lock box connectors, which allow for high energy efficiency due to lower resistance.
Terminals with insulation crimp, like ground lug (GL), also known as eyelet terminals, will require installing the crimping module to the standard MPX-TC.
GL terminal with multiple wires
The GL terminal is used to connect multiple ground wires together in one location. An automotive harness can have over 10 GL terminals depending on the vehicle complexity. But they all come in different shapes for mounting on the automobile chassis. These traditional terminals are available in 4 and 7 mm (inside wall width), with a maximum of 20 mm² total cross-sectional area for all wires. Recently, some OEMs are using newer GL terminals that have no walls and are flat. The trend in the harnesses is that there will be more GL terminals in the future. In either case, the MPX welder can easily switch from one with walls to flat versions.
Flat terminals on the reel (carrier strip) will require the feeding unit module, the reel mount, and the contact strip separator, as well as a sonotrode and a nest.
Lear MAK Terminal with 16 mm²
MAK terminals designed and produced by Lear corporation are another popular connection system in automotive wire harnesses. There could be as many as 10 terminals in the harness for north American automobiles and perhaps more for European cars. It is mostly used for following modules in a typical automobile:
- Perfuse centers: harness connection to fuse arrays
- Cooling/rad fan: pigtail or inline connection
- Power steering
- E-turbo charger
- Pluggable power feeds to IP distribution boxes
MAK terminals are available as MAK12 or MAK8 and have been used primarily on low voltage applications. The MAK12 is specified for cables up to 35 mm². This terminal is now used more often for high voltage (HV) applications and in electric vehicles than for low voltage applications in the harness. In one of the future car programs, the battery distribution unit has 10 MAK terminals as part of the design. It is normally available on a reel. Therefore, the MPX machine uses the feeding unit as well as the terminal separator in the welding area.
Simplicity of a universal welding machine cannot be achieved without well thought and established operating software. This is the reason that equipment manufacturers have invested in developing better software in the last few years. Telsonic developed a universal software that can work with all Telsonic welding equipment including the MPX-TC. Telso®Flex with its intuitive HMI touch screen, makes the changeover and operation even easier and more reliable. The Telso®Flex is a pioneering controls technology with a high-level quality monitoring, machine troubleshooting, and networking from remote location.
The demands on a system control can change over time due to adjustments in the production environment. For example, adjustments to the process workflows require different interfaces, or a different operating language is needed due to production relocations. Due to its modern architecture, the Telso®Flex software can be adapted to these needs and upgraded with add-ons. New functions can also be installed later.
Productivity is affected in several ways. The Telso®Flex offers various functions to increase quality and optimize process times. It starts with the design of the application for process-reliable parameters. During production, the quality must be continuously monitored, and trends must be recognized. In this way, an impending production failure can be recognized and avoided. When producing large batches, the batch size of the packaging unit can also be specified, and the operator can be informed to provide support. The software offers topic-related assistance for maintenance and servicing to shorten the unproductive time.
For traceability and quality control, all welds, including all parameters and results, are logged. This log can be saved locally, on a USB stick, network or FTP drive and updated continuously.
If assistance is needed, the error log can be exported and analyzed by Telsonic. This means that global support is provided quickly and efficiently.
The universal and modular features of the MPX with a power range of 2.4KW to 7.2 KW allows the capability of a wider range of applications with the same machine
In a wider spectrum, there are applications involving flat bus bar to larger cables, smaller area for the specific cable size, and short cables, where the vibrations may affect the connection at the other end of the cable. In addition, geometrical shapes or much larger cables will require special welding equipment. Here are some examples of other applications utilized by the industry.
For additional information and evaluation of your applications, please
visit us at www.telsonic.com or contact our USA branch in Massachusetts -617 244 0400